From molecular targets to cellular targets
From molecular targets to cellular targets
With the development of molecular biology, we understood that changes in sequence and expression of genes can cause several diseases. As such, from approaches targeting “molecules” such as therapies using small molecules and antibody therapy, a new approach targeting “cells” such as gene supplementation, gene editing, and cell transplantation have been developed.
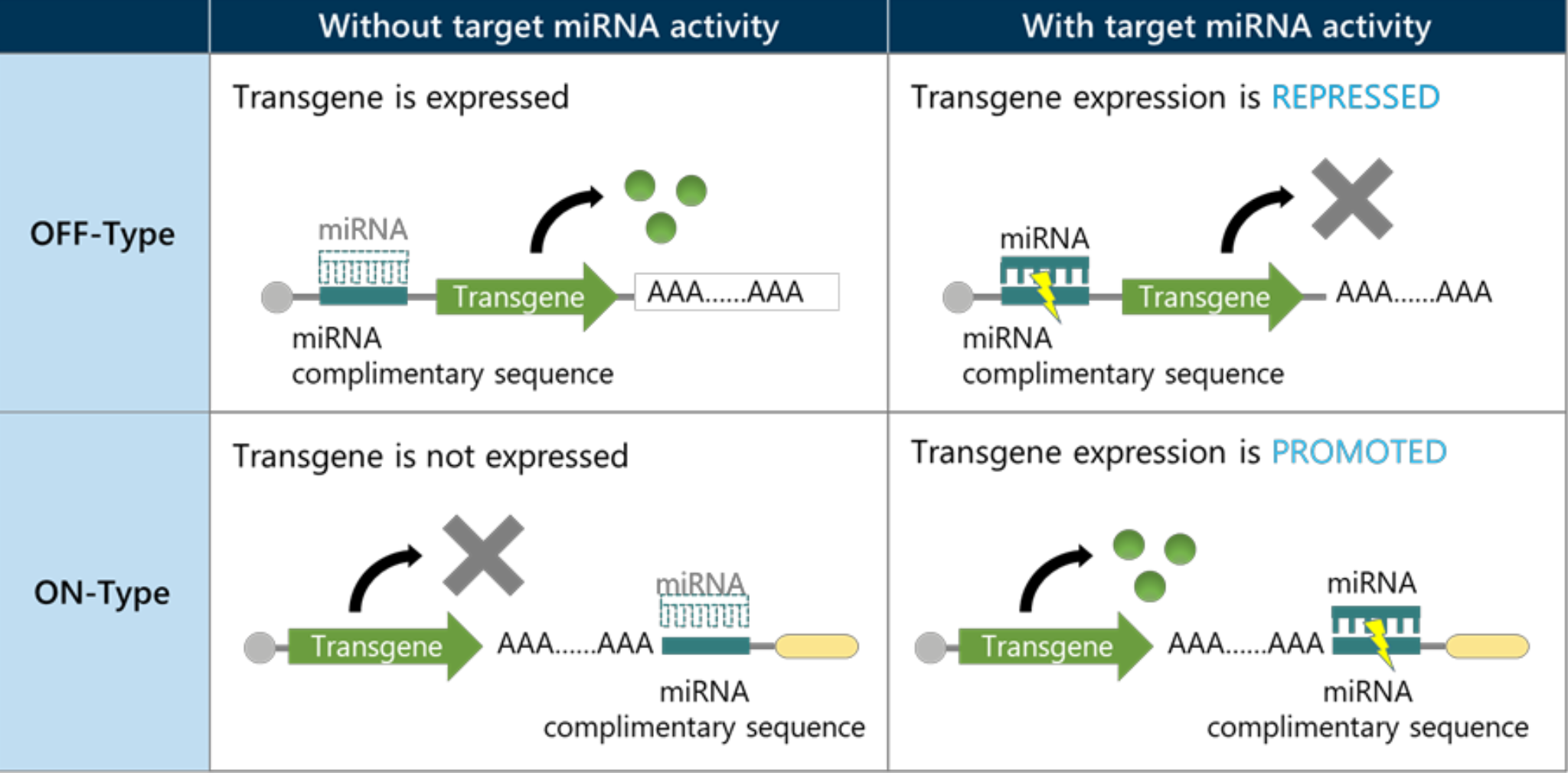
However, for such strategies to be effective, we need to address their targetability to specific cells.
In gene therapy, we must consider unexpected side-effects on healthy cells, which may diminish a treatment approach due to safety concerns; lowering efficiency and efficacy. Despite the causes of a disease being identified and viable approaches being developed, the therapeutic applicability of such methods can be limited due to low specificity.
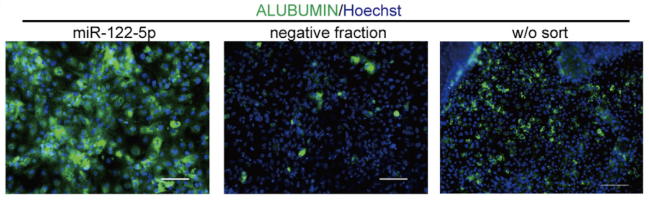
Furthermore, low specificity also has negative effects on the cells of a high enough purity for transplantation, limiting the usefulness of transplantation in clinical settings, as it can be difficult to guarantee that transplanted cells will not evolve into tumors.
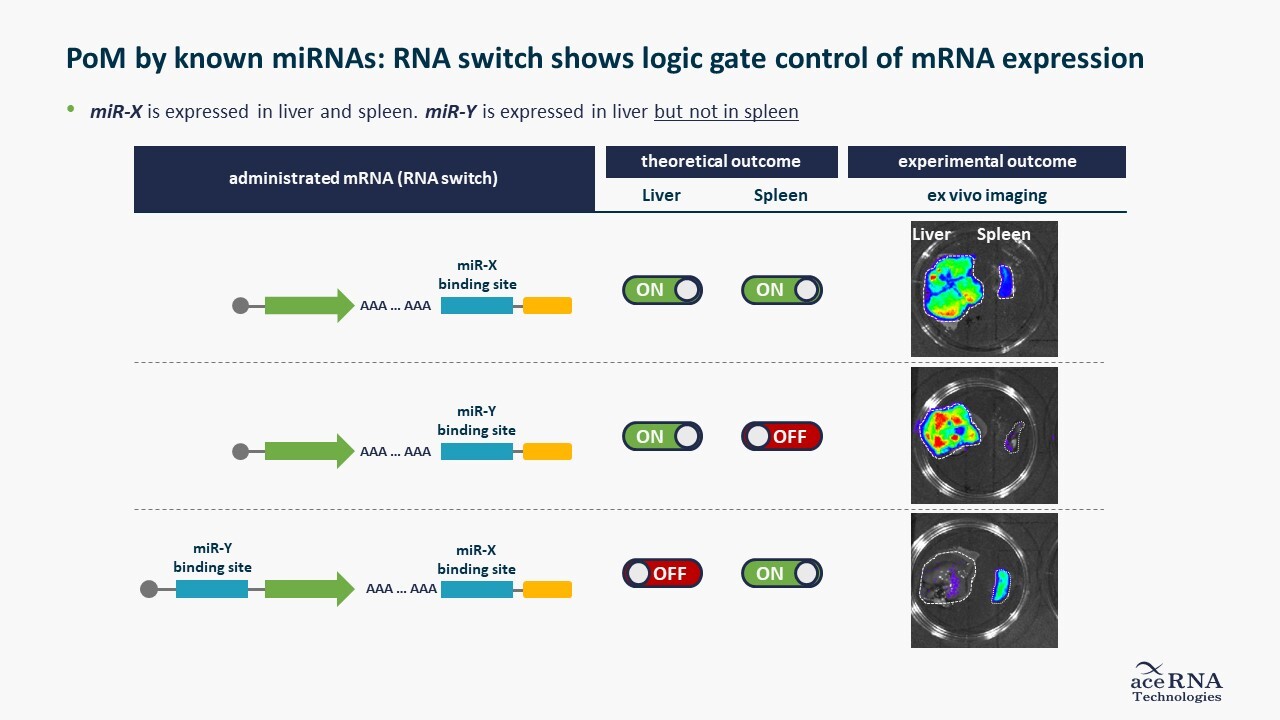
This means there is a growing need for a technology that allows us to generate, treat and target “specific cells”.